Web 扩展
Visual Studio Code 可以作为浏览器中的编辑器运行。一个例子是 github.dev 用户界面,它可以通过在 GitHub 中浏览存储库或拉取请求时按 .(句点键)来访问。当 VS Code 在 Web 中使用时,已安装的扩展会在浏览器中的扩展宿主中运行,称为“Web 扩展宿主”。可以在 Web 扩展宿主中运行的扩展称为“Web 扩展”。
Web 扩展与常规扩展具有相同的结构,但由于运行时不同,它们不与为 Node.js 运行时编写的扩展运行相同的代码。Web 扩展仍然可以访问完整的 VS Code API,但不再能访问 Node.js API 和模块加载。相反,Web 扩展受到浏览器沙盒的限制,因此与普通扩展相比具有限制。
Web 扩展运行时在 VS Code 桌面版上也受支持。如果您决定将扩展创建为 Web 扩展,它将在Web 版 VS Code(包括 vscode.dev 和 github.dev)以及桌面版和 GitHub Codespaces 等服务中得到支持。
Web 扩展的构成
Web 扩展的结构与常规扩展类似。扩展清单(package.json)定义了扩展源代码的入口文件并声明了扩展贡献。
对于 Web 扩展,主入口文件由 browser 属性定义,而不是像常规扩展那样由 main 属性定义。
contributes 属性对于 Web 扩展和常规扩展的工作方式相同。
以下示例显示了一个简单的 Hello World 扩展的 package.json,它仅在 Web 扩展宿主中运行(它只有一个 browser 入口点)。
{
"name": "helloworld-web-sample",
"displayName": "helloworld-web-sample",
"description": "HelloWorld example for VS Code in the browser",
"version": "0.0.1",
"publisher": "vscode-samples",
"repository": "https://github.com/microsoft/vscode-extension-samples/helloworld-web-sample",
"engines": {
"vscode": "^1.74.0"
},
"categories": ["Other"],
"activationEvents": [],
"browser": "./dist/web/extension.js",
"contributes": {
"commands": [
{
"command": "helloworld-web-sample.helloWorld",
"title": "Hello World"
}
]
},
"scripts": {
"vscode:prepublish": "npm run package-web",
"compile-web": "webpack",
"watch-web": "webpack --watch",
"package-web": "webpack --mode production --devtool hidden-source-map"
},
"devDependencies": {
"@types/vscode": "^1.59.0",
"ts-loader": "^9.2.2",
"webpack": "^5.38.1",
"webpack-cli": "^4.7.0",
"@types/webpack-env": "^1.16.0",
"process": "^0.11.10"
}
}
注意:如果您的扩展目标是 1.74 版之前的 VS Code,您必须在
activationEvents中明确列出onCommand:helloworld-web-sample.helloWorld。
只有 main 入口点但没有 browser 的扩展不是 Web 扩展。它们会被 Web 扩展宿主忽略,并且不能在扩展视图中下载。
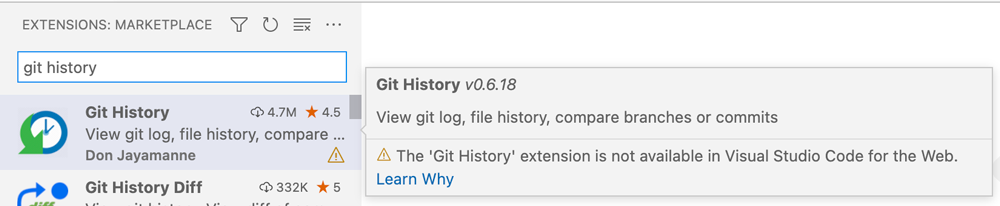
只有声明性贡献(只有 contributes,没有 main 或 browser)的扩展可以是 Web 扩展。它们可以在Web 版 VS Code 中安装和运行,而无需扩展作者进行任何修改。具有声明性贡献的扩展示例包括主题、语法和代码片段。
扩展可以同时具有 browser 和 main 入口点,以便在浏览器和 Node.js 运行时中运行。将现有扩展更新为 Web 扩展部分展示了如何将扩展迁移到在两种运行时中工作。
Web 扩展启用部分列出了用于决定扩展是否可以在 Web 扩展宿主中加载的规则。
Web 扩展主文件
Web 扩展的主文件由 browser 属性定义。该脚本在 Web 扩展宿主中的 浏览器 WebWorker 环境中运行。它受到浏览器 Worker 沙盒的限制,与在 Node.js 运行时中运行的普通扩展相比具有限制。
- 不支持导入或要求其他模块。
importScripts也不可用。因此,代码必须打包成单个文件。 - VS Code API 可以通过模式
require('vscode')加载。这将有效,因为存在一个用于require的 shim,但此 shim 不能用于加载额外的扩展文件或额外的 Node 模块。它只适用于require('vscode')。 - Node.js 全局变量和库(如
process、os、setImmediate、path、util、url)在运行时不可用。但是,它们可以通过像 webpack 这样的工具添加。webpack 配置部分解释了如何实现这一点。 - 打开的工作区或文件夹位于虚拟文件系统上。访问工作区文件需要通过 VS Code 文件系统 API,该 API 可通过
vscode.workspace.fs访问。 - 扩展上下文位置(
ExtensionContext.extensionUri)和存储位置(ExtensionContext.storageUri、globalStorageUri)也位于虚拟文件系统上,需要通过vscode.workspace.fs访问。 - 为了访问 Web 资源,必须使用 Fetch API。访问的资源需要支持 跨域资源共享 (CORS)。
- 无法创建子进程或运行可执行文件。但是,可以通过 Worker API 创建 Web Worker。这用于运行语言服务器,如Web 扩展中的语言服务器协议部分所述。
- 与常规扩展一样,扩展的
activate/deactivate函数需要通过模式exports.activate = ...导出。
开发 Web 扩展
值得庆幸的是,TypeScript 和 webpack 等工具可以隐藏许多浏览器运行时限制,让您可以像编写常规扩展一样编写 Web 扩展。Web 扩展和常规扩展通常可以从相同的源代码生成。
例如,yo code 生成器创建的 Hello Web 扩展仅在构建脚本上有所不同。您可以使用通过调试:选择并开始调试命令访问的启动配置,像传统 Node.js 扩展一样运行和调试生成的扩展。
创建 Web 扩展
要搭建新的 Web 扩展,请使用 yo code 并选择新建 Web 扩展。确保已安装最新版本的 generator-code (>= generator-code@1.6)。要更新生成器和 yo,请运行 npm i -g yo generator-code。
创建的扩展包括扩展的源代码(一个显示 Hello World 通知命令)、package.json 清单文件和 webpack 或 esbuild 配置文件。
为了简化起见,我们假设您使用 webpack 作为打包器。在文章的最后,我们还将解释选择 esbuild 时有什么不同。
src/web/extension.ts是扩展的入口源代码文件。它与常规的 hello 扩展相同。package.json是扩展清单。- 它使用
browser属性指向入口文件。 - 它提供了脚本:
compile-web、watch-web和package-web用于编译、监视和打包。
- 它使用
webpack.config.js是 webpack 配置文件,它将扩展源代码编译并捆绑成一个文件。.vscode/launch.json包含在 VS Code 桌面版中运行 Web 扩展和测试的启动配置,其中包含 Web 扩展宿主(不再需要设置extensions.webWorker)。.vscode/task.json包含启动配置使用的构建任务。它使用npm run watch-web并依赖于 webpack 特定的ts-webpack-watch问题匹配器。.vscode/extensions.json包含提供问题匹配器的扩展。这些扩展需要安装才能使启动配置正常工作。tsconfig.json定义了与webworker运行时匹配的编译选项。
helloworld-web-sample 中的源代码与生成器创建的源代码类似。
Webpack 配置
webpack 配置文件由 yo code 自动生成。它将您的扩展源代码捆绑到一个 JavaScript 文件中,以便在 Web 扩展宿主中加载。
稍后我们将解释如何使用 esbuild 作为打包器,但现在我们从 webpack 开始。
const path = require('path');
const webpack = require('webpack');
/** @typedef {import('webpack').Configuration} WebpackConfig **/
/** @type WebpackConfig */
const webExtensionConfig = {
mode: 'none', // this leaves the source code as close as possible to the original (when packaging we set this to 'production')
target: 'webworker', // extensions run in a webworker context
entry: {
extension: './src/web/extension.ts', // source of the web extension main file
'test/suite/index': './src/web/test/suite/index.ts' // source of the web extension test runner
},
output: {
filename: '[name].js',
path: path.join(__dirname, './dist/web'),
libraryTarget: 'commonjs',
devtoolModuleFilenameTemplate: '../../[resource-path]'
},
resolve: {
mainFields: ['browser', 'module', 'main'], // look for `browser` entry point in imported node modules
extensions: ['.ts', '.js'], // support ts-files and js-files
alias: {
// provides alternate implementation for node module and source files
},
fallback: {
// Webpack 5 no longer polyfills Node.js core modules automatically.
// see https://webpack.js.cn/configuration/resolve/#resolvefallback
// for the list of Node.js core module polyfills.
assert: require.resolve('assert')
}
},
module: {
rules: [
{
test: /\.ts$/,
exclude: /node_modules/,
use: [
{
loader: 'ts-loader'
}
]
}
]
},
plugins: [
new webpack.ProvidePlugin({
process: 'process/browser' // provide a shim for the global `process` variable
})
],
externals: {
vscode: 'commonjs vscode' // ignored because it doesn't exist
},
performance: {
hints: false
},
devtool: 'nosources-source-map' // create a source map that points to the original source file
};
module.exports = [webExtensionConfig];
webpack.config.js 的一些重要字段是:
entry字段包含您的扩展和测试套件的主要入口点。- 您可能需要调整此路径以正确指向您的扩展的入口点。
- 对于现有扩展,您可以首先将此路径指向您当前用于
package.json中main的文件。 - 如果您不想打包您的测试,可以省略测试套件字段。
output字段指示编译文件将位于何处。[name]将被entry中使用的键替换。因此在生成的配置文件中,它将生成dist/web/extension.js和dist/web/test/suite/index.js。
target字段指示编译后的 JavaScript 文件将运行的环境类型。对于 Web 扩展,您希望此值为webworker。resolve字段包含为在浏览器中无法运行的 Node 库添加别名和回退的功能。- 如果您正在使用像
path这样的库,您可以指定如何在 Web 编译上下文中解析path。例如,您可以指向项目中定义path的文件,例如path: path.resolve(__dirname, 'src/my-path-implementation-for-web.js')。或者您可以使用 Browserify 打包的 Node 版本库path-browserify并指定path: require.resolve('path-browserify')。 - 有关 Node.js 核心模块 polyfills 的列表,请参阅 webpack resolve.fallback。
- 如果您正在使用像
plugins部分使用 DefinePlugin 插件来 polyfill 诸如processNode.js 全局变量等全局变量。
测试您的 Web 扩展
目前有三种方法可以在将 Web 扩展发布到市场之前对其进行测试。
- 使用在桌面版上运行的 VS Code,并使用
--extensionDevelopmentKind=web选项在 VS Code 中运行 Web 扩展宿主中运行您的 Web 扩展。 - 使用 @vscode/test-web Node 模块打开一个包含 Web 版 VS Code 的浏览器,其中包括您的扩展,通过本地服务器提供。
- 侧载您的扩展到 vscode.dev,以在实际环境中查看您的扩展。
在桌面版 VS Code 中测试您的 Web 扩展
为了使用现有的 VS Code 扩展开发体验,桌面版 VS Code 支持运行 Web 扩展宿主以及常规 Node.js 扩展宿主。
使用“新建 Web 扩展”生成器提供的 pwa-extensionhost 启动配置。
{
"version": "0.2.0",
"configurations": [
{
"name": "Run Web Extension in VS Code",
"type": "pwa-extensionHost",
"debugWebWorkerHost": true,
"request": "launch",
"args": [
"--extensionDevelopmentPath=${workspaceFolder}",
"--extensionDevelopmentKind=web"
],
"outFiles": ["${workspaceFolder}/dist/web/**/*.js"],
"preLaunchTask": "npm: watch-web"
}
]
}
它使用任务 npm: watch-web 通过调用 npm run watch-web 来编译扩展。该任务应该在 tasks.json 中。
{
"version": "2.0.0",
"tasks": [
{
"type": "npm",
"script": "watch-web",
"group": "build",
"isBackground": true,
"problemMatcher": ["$ts-webpack-watch"]
}
]
}
$ts-webpack-watch 是一个问题匹配器,可以解析 webpack 工具的输出。它由 TypeScript + Webpack Problem Matchers 扩展提供。
在启动的扩展开发宿主实例中,Web 扩展将在 Web 扩展宿主中可用并运行。运行 Hello World 命令以激活扩展。
打开运行中的扩展视图(命令:开发人员:显示运行中的扩展)以查看哪些扩展正在 Web 扩展宿主中运行。
使用 @vscode/test-web 在浏览器中测试您的 Web 扩展
@vscode/test-web Node 模块提供了一个 CLI 和 API,用于在浏览器中测试 Web 扩展。
该 Node 模块贡献了一个 npm 二进制文件 vscode-test-web,可以从命令行打开 Web 版 VS Code。
- 它将 VS Code 的 Web 部分下载到
.vscode-test-web。 - 在
localhost:3000上启动本地服务器。 - 打开浏览器(Chromium、Firefox 或 Webkit)。
您可以从命令行运行它。
npx @vscode/test-web --extensionDevelopmentPath=$extensionFolderPath $testDataPath
或者更好的是,将 @vscode/test-web 添加为您的扩展的开发依赖项并在脚本中调用它。
"devDependencies": {
"@vscode/test-web": "*"
},
"scripts": {
"open-in-browser": "vscode-test-web --extensionDevelopmentPath=. ."
}
查看 @vscode/test-web README 以获取更多 CLI 选项。
| 选项 | 参数说明 |
|---|---|
| --browserType | 要启动的浏览器:chromium(默认)、firefox 或 webkit |
| --extensionDevelopmentPath | 指向正在开发的扩展的路径,以包括该扩展。 |
| --extensionTestsPath | 指向要运行的测试模块的路径。 |
| --permission | 授予打开的浏览器的权限:例如 clipboard-read, clipboard-write。请参阅 完整选项列表。参数可以提供多次。 |
| --folder-uri | 在 VS Code 上打开的工作区 URI。如果提供了 folderPath,则忽略。 |
| --extensionPath | 指向包含要包含的其他扩展的文件夹的路径。 参数可以提供多次。 |
| folderPath | 要在 VS Code 上打开的本地文件夹。 文件夹内容将作为虚拟文件系统可用,并作为工作区打开。 |
VS Code 的 Web 部分下载到 .vscode-test-web 文件夹。您希望将其添加到您的 .gitignore 文件中。
在 vscode.dev 中测试您的 Web 扩展
在您将扩展发布供大家在 Web 版 VS Code 上使用之前,您可以验证您的扩展在实际的 vscode.dev 环境中的行为。
要在 vscode.dev 上查看您的扩展,您首先需要从您的机器托管它,以便 vscode.dev 下载并运行。
首先,您需要安装 mkcert。
然后,将 localhost.pem 和 localhost-key.pem 文件生成到您不会丢失它们的位置(例如 $HOME/certs)。
$ mkdir -p $HOME/certs
$ cd $HOME/certs
$ mkcert -install
$ mkcert localhost
然后,从您的扩展路径启动一个 HTTP 服务器,运行 npx serve。
$ npx serve --cors -l 5000 --ssl-cert $HOME/certs/localhost.pem --ssl-key $HOME/certs/localhost-key.pem
npx: installed 78 in 2.196s
┌────────────────────────────────────────────────────┐
│ │
│ Serving! │
│ │
│ - Local: https://:5000 │
│ - On Your Network: https://172.19.255.26:5000 │
│ │
│ Copied local address to clipboard! │
│ │
└────────────────────────────────────────────────────┘
最后,打开 vscode.dev,从命令面板 (⇧⌘P (Windows, Linux Ctrl+Shift+P)) 运行开发人员:从位置安装扩展...,粘贴上面的 URL,示例中为 https://:5000,然后选择安装。
检查日志
您可以检查浏览器开发人员工具控制台中的日志,以查看扩展中的任何错误、状态和日志。
您可能会看到 vscode.dev 本身的其他日志。此外,您无法轻松设置断点也无法查看扩展的源代码。这些限制使得在 vscode.dev 中调试并不是最愉快的体验,因此我们建议在侧载到 vscode.dev 之前使用前两种测试选项。侧载是发布扩展前一个很好的最终健全性检查。
Web 扩展测试
支持 Web 扩展测试,并且可以像常规扩展测试一样实现。请参阅测试扩展文章以了解扩展测试的基本结构。
@vscode/test-web Node 模块相当于 @vscode/test-electron(以前名为 vscode-test)。它允许您在 Chromium、Firefox 和 Safari 上从命令行运行扩展测试。
该实用程序执行以下步骤:
- 从本地 Web 服务器启动 Web 版 VS Code 编辑器。
- 打开指定的浏览器。
- 运行提供的测试运行器脚本。
您可以在持续构建中运行测试,以确保扩展在所有浏览器上都能正常工作。
测试运行器脚本在 Web 扩展主机上运行,其限制与Web 扩展主文件相同。
- 所有文件都捆绑成一个文件。它应该包含测试运行器(例如 Mocha)和所有测试(通常是
*.test.ts)。 - 只支持
require('vscode')。
由 yo code Web 扩展生成器创建的 webpack 配置有一个测试部分。它期望测试运行器脚本位于 ./src/web/test/suite/index.ts。提供的 测试运行器脚本 使用 Mocha 的 Web 版本,并包含 webpack 特定的语法来导入所有测试文件。
require('mocha/mocha'); // import the mocha web build
export function run(): Promise<void> {
return new Promise((c, e) => {
mocha.setup({
ui: 'tdd',
reporter: undefined
});
// bundles all files in the current directory matching `*.test`
const importAll = (r: __WebpackModuleApi.RequireContext) => r.keys().forEach(r);
importAll(require.context('.', true, /\.test$/));
try {
// Run the mocha test
mocha.run(failures => {
if (failures > 0) {
e(new Error(`${failures} tests failed.`));
} else {
c();
}
});
} catch (err) {
console.error(err);
e(err);
}
});
}
要从命令行运行 Web 测试,请将以下内容添加到您的 package.json 并使用 npm test 运行它。
"devDependencies": {
"@vscode/test-web": "*"
},
"scripts": {
"test": "vscode-test-web --extensionDevelopmentPath=. --extensionTestsPath=dist/web/test/suite/index.js"
}
要在带有测试数据的文件夹上打开 VS Code,请将本地文件夹路径 (folderPath) 作为最后一个参数传递。
要在 VS Code (Insiders) 桌面版中运行(和调试)扩展测试,请使用 Extension Tests in VS Code 启动配置。
{
"version": "0.2.0",
"configurations": [
{
"name": "Extension Tests in VS Code",
"type": "extensionHost",
"debugWebWorkerHost": true,
"request": "launch",
"args": [
"--extensionDevelopmentPath=${workspaceFolder}",
"--extensionDevelopmentKind=web",
"--extensionTestsPath=${workspaceFolder}/dist/web/test/suite/index"
],
"outFiles": ["${workspaceFolder}/dist/web/**/*.js"],
"preLaunchTask": "npm: watch-web"
}
]
}
发布 Web 扩展
Web 扩展与其他扩展一起托管在 Marketplace 上。
请务必使用最新版本的 vsce 发布您的扩展。vsce 标记所有 Web 扩展。为此,vsce 使用Web 扩展启用部分中列出的规则。
将现有扩展更新为 Web 扩展
无代码扩展
没有代码,只有贡献点(例如,主题、片段和基本语言扩展)的扩展不需要任何修改。它们可以在 Web 扩展宿主中运行,并且可以从扩展视图中安装。
无需重新发布,但在发布新版本的扩展时,请务必使用最新版本的 vsce。
迁移带有代码的扩展
具有源代码(由 main 属性定义)的扩展需要提供Web 扩展主文件并在 package.json 中设置 browser 属性。
请按照以下步骤重新编译您的扩展代码以适应浏览器环境:
- 如webpack 配置部分所示,添加一个 webpack 配置文件。如果您已经为 Node.js 扩展代码创建了 webpack 文件,您可以为 Web 添加一个新部分。请参阅 vscode-css-formatter 作为示例。
- 添加 测试您的 Web 扩展 部分所示的
launch.json和tasks.json文件。 - 在 webpack 配置文件中,将输入文件设置为现有的 Node.js 主文件,或者为 Web 扩展创建新的主文件。
- 在
package.json中,添加 Web 扩展结构 部分所示的browser和scripts属性。 - 运行
npm run compile-web来调用 webpack,并查看需要做哪些工作才能使您的扩展在 Web 中运行。
为了确保尽可能多的源代码可以重用,这里有一些技巧:
- 要 polyfill 像
path这样的 Node.js 核心模块,请向 resolve.fallback 添加一个条目。 - 要提供像
process这样的 Node.js 全局变量,请使用 DefinePlugin 插件。 - 使用在浏览器和 Node 运行时中都有效的 Node 模块。Node 模块可以通过同时定义
browser和main入口点来做到这一点。Webpack 会自动使用与其目标匹配的入口点。执行此操作的 Node 模块示例有 request-light 和 @vscode/l10n。 - 要为 Node 模块或源文件提供替代实现,请使用 resolve.alias。
- 将您的代码分为浏览器部分、Node.js 部分和公共部分。在公共部分中,只使用在浏览器和 Node.js 运行时中都有效的代码。为在 Node.js 和浏览器中具有不同实现的功能创建抽象。
- 注意
path、URI.file、context.extensionPath、rootPath、uri.fsPath的用法。这些在 Web 版 VS Code 中使用的虚拟工作区(非文件系统)中不起作用。相反,请使用带有URI.parse、context.extensionUri的 URI。vscode-uri Node 模块提供了joinPath、dirName、baseName、extName、resolvePath。 - 注意
fs的用法。将其替换为使用 vscodeworkspace.fs。
当您的扩展在 Web 中运行时,提供较少的功能是可以的。使用when 子句上下文来控制在 Web 上运行的虚拟工作区中哪些命令、视图和任务可用或隐藏。
- 使用
virtualWorkspace上下文变量来判断当前工作区是否为非文件系统工作区。 - 使用
resourceScheme检查当前资源是否为file资源。 - 如果存在平台 shell,则使用
shellExecutionSupported。 - 实现替代命令处理程序,显示一个对话框来解释该命令不适用的原因。
WebWorker 可以作为分叉进程的替代方案。我们已经更新了多个语言服务器,使其作为 Web 扩展运行,包括内置的 JSON、CSS 和 HTML 语言服务器。下面的语言服务器协议部分提供了更多详细信息。
浏览器运行时环境仅支持 JavaScript 和 WebAssembly 的执行。用其他编程语言编写的库需要交叉编译,例如有用于将 C/C++ 和 Rust 编译为 WebAssembly 的工具。vscode-anycode 扩展就是一个例子,它使用 tree-sitter,这是一个编译为 WebAssembly 的 C/C++ 代码。
Web 扩展中的语言服务器协议
vscode-languageserver-node 是 语言服务器协议 (LSP) 的实现,用作语言服务器实现的基础,例如 JSON、CSS 和 HTML。
自 3.16.0 版以来,客户端和服务器现在也提供了浏览器实现。服务器可以在 Web Worker 中运行,并且连接基于 Web Worker 的 postMessage 协议。
浏览器客户端可以在 'vscode-languageclient/browser' 中找到。
import { LanguageClient } from `vscode-languageclient/browser`;
服务器在 vscode-languageserver/browser 中。
lsp-web-extension-sample 展示了这是如何工作的。
Web 扩展启用
如果满足以下条件,VS Code 会自动将扩展视为 Web 扩展:
- 扩展清单 (
package.json) 具有browser入口点。 - 扩展清单没有
main入口点,也没有以下任何贡献点:localizations、debuggers、terminal、typescriptServerPlugins。
如果扩展想要提供一个也在 Web 扩展主机中工作的调试器或终端,则需要定义一个 browser 入口点。
使用 ESBuild
如果您想使用 esbuild 而不是 webpack,请执行以下操作:
添加一个 esbuild.js 构建脚本。
const esbuild = require('esbuild');
const glob = require('glob');
const path = require('path');
const polyfill = require('@esbuild-plugins/node-globals-polyfill');
const production = process.argv.includes('--production');
const watch = process.argv.includes('--watch');
async function main() {
const ctx = await esbuild.context({
entryPoints: ['src/web/extension.ts', 'src/web/test/suite/extensionTests.ts'],
bundle: true,
format: 'cjs',
minify: production,
sourcemap: !production,
sourcesContent: false,
platform: 'browser',
outdir: 'dist/web',
external: ['vscode'],
logLevel: 'warning',
// Node.js global to browser globalThis
define: {
global: 'globalThis'
},
plugins: [
polyfill.NodeGlobalsPolyfillPlugin({
process: true,
buffer: true
}),
testBundlePlugin,
esbuildProblemMatcherPlugin /* add to the end of plugins array */
]
});
if (watch) {
await ctx.watch();
} else {
await ctx.rebuild();
await ctx.dispose();
}
}
/**
* For web extension, all tests, including the test runner, need to be bundled into
* a single module that has a exported `run` function .
* This plugin bundles implements a virtual file extensionTests.ts that bundles all these together.
* @type {import('esbuild').Plugin}
*/
const testBundlePlugin = {
name: 'testBundlePlugin',
setup(build) {
build.onResolve({ filter: /[\/\\]extensionTests\.ts$/ }, args => {
if (args.kind === 'entry-point') {
return { path: path.resolve(args.path) };
}
});
build.onLoad({ filter: /[\/\\]extensionTests\.ts$/ }, async args => {
const testsRoot = path.join(__dirname, 'src/web/test/suite');
const files = await glob.glob('*.test.{ts,tsx}', { cwd: testsRoot, posix: true });
return {
contents:
`export { run } from './mochaTestRunner.ts';` +
files.map(f => `import('./${f}');`).join(''),
watchDirs: files.map(f => path.dirname(path.resolve(testsRoot, f))),
watchFiles: files.map(f => path.resolve(testsRoot, f))
};
});
}
};
/**
* This plugin hooks into the build process to print errors in a format that the problem matcher in
* Visual Studio Code can understand.
* @type {import('esbuild').Plugin}
*/
const esbuildProblemMatcherPlugin = {
name: 'esbuild-problem-matcher',
setup(build) {
build.onStart(() => {
console.log('[watch] build started');
});
build.onEnd(result => {
result.errors.forEach(({ text, location }) => {
console.error(`✘ [ERROR] ${text}`);
if (location == null) return;
console.error(` ${location.file}:${location.line}:${location.column}:`);
});
console.log('[watch] build finished');
});
}
};
main().catch(e => {
console.error(e);
process.exit(1);
});
构建脚本执行以下操作:
- 它使用 esbuild 创建一个构建上下文。上下文配置为:
- 将
src/web/extension.ts中的代码捆绑到一个文件dist/web/extension.js中。 - 将所有测试,包括测试运行器 (mocha),捆绑到一个文件
dist/web/test/suite/extensionTests.js中。 - 如果传递了
--production标志,则压缩代码。 - 除非传递了
--production标志,否则生成源映射。 - 将 'vscode' 模块从捆绑包中排除(因为它由 VS Code 运行时提供)。
- 为
process和buffer创建 polyfills。 - 使用 esbuildProblemMatcherPlugin 插件报告阻止打包程序完成的错误。此插件以一种格式发出错误,该格式可由
esbuild问题匹配器检测到,该匹配器也需要作为扩展安装。 - 使用 testBundlePlugin 实现一个测试主文件 (
extensionTests.js),该文件引用所有测试文件和 mocha 测试运行器mochaTestRunner.js。
- 将
- 如果传递了
--watch标志,它会开始监视源文件的更改,并在检测到更改时重新构建捆绑包。
esbuild 可以直接处理 TypeScript 文件。但是,esbuild 只是剥离所有类型声明而不进行任何类型检查。仅报告语法错误,并可能导致 esbuild 失败。
因此,我们单独运行 TypeScript 编译器 (tsc) 来检查类型,但不发出任何代码(标志 --noEmit)。
package.json 中的 scripts 部分现在看起来是这样的:
"scripts": {
"vscode:prepublish": "npm run package-web",
"compile-web": "npm run check-types && node esbuild.js",
"watch-web": "npm-run-all -p watch-web:*",
"watch-web:esbuild": "node esbuild.js --watch",
"watch-web:tsc": "tsc --noEmit --watch --project tsconfig.json",
"package-web": "npm run check-types && node esbuild.js --production",
"check-types": "tsc --noEmit",
"pretest": "npm run compile-web",
"test": "vscode-test-web --browserType=chromium --extensionDevelopmentPath=. --extensionTestsPath=dist/web/test/suite/extensionTests.js",
"run-in-browser": "vscode-test-web --browserType=chromium --extensionDevelopmentPath=. ."
}
npm-run-all 是一个 Node 模块,它并行运行名称与给定前缀匹配的脚本。对我们来说,它运行 watch-web:esbuild 和 watch-web:tsc 脚本。您需要将 npm-run-all 添加到 package.json 中的 devDependencies 部分。
以下 tasks.json 文件为每个监视任务提供了单独的终端:
{
"version": "2.0.0",
"tasks": [
{
"label": "watch-web",
"dependsOn": ["npm: watch-web:tsc", "npm: watch-web:esbuild"],
"presentation": {
"reveal": "never"
},
"group": {
"kind": "build",
"isDefault": true
},
"runOptions": {
"runOn": "folderOpen"
}
},
{
"type": "npm",
"script": "watch-web:esbuild",
"group": "build",
"problemMatcher": "$esbuild-watch",
"isBackground": true,
"label": "npm: watch-web:esbuild",
"presentation": {
"group": "watch",
"reveal": "never"
}
},
{
"type": "npm",
"script": "watch-web:tsc",
"group": "build",
"problemMatcher": "$tsc-watch",
"isBackground": true,
"label": "npm: watch-web:tsc",
"presentation": {
"group": "watch",
"reveal": "never"
}
},
{
"label": "compile",
"type": "npm",
"script": "compile-web",
"problemMatcher": ["$tsc", "$esbuild"]
}
]
}
这是 esbuild 构建脚本中引用的 mochaTestRunner.js。
// Imports mocha for the browser, defining the `mocha` global.
import 'mocha/mocha';
mocha.setup({
ui: 'tdd',
reporter: undefined
});
export function run(): Promise<void> {
return new Promise((c, e) => {
try {
// Run the mocha test
mocha.run(failures => {
if (failures > 0) {
e(new Error(`${failures} tests failed.`));
} else {
c();
}
});
} catch (err) {
console.error(err);
e(err);
}
});
}