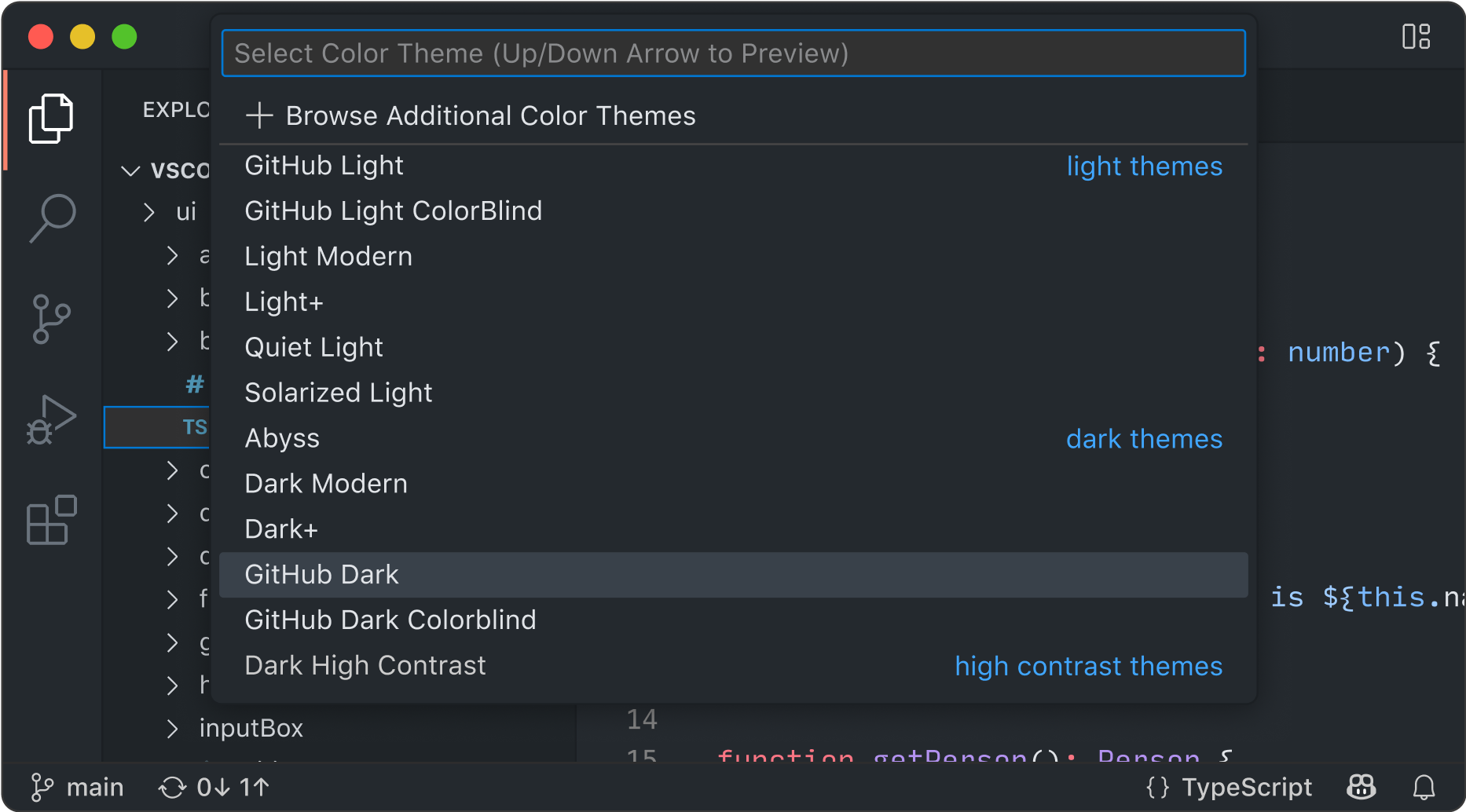
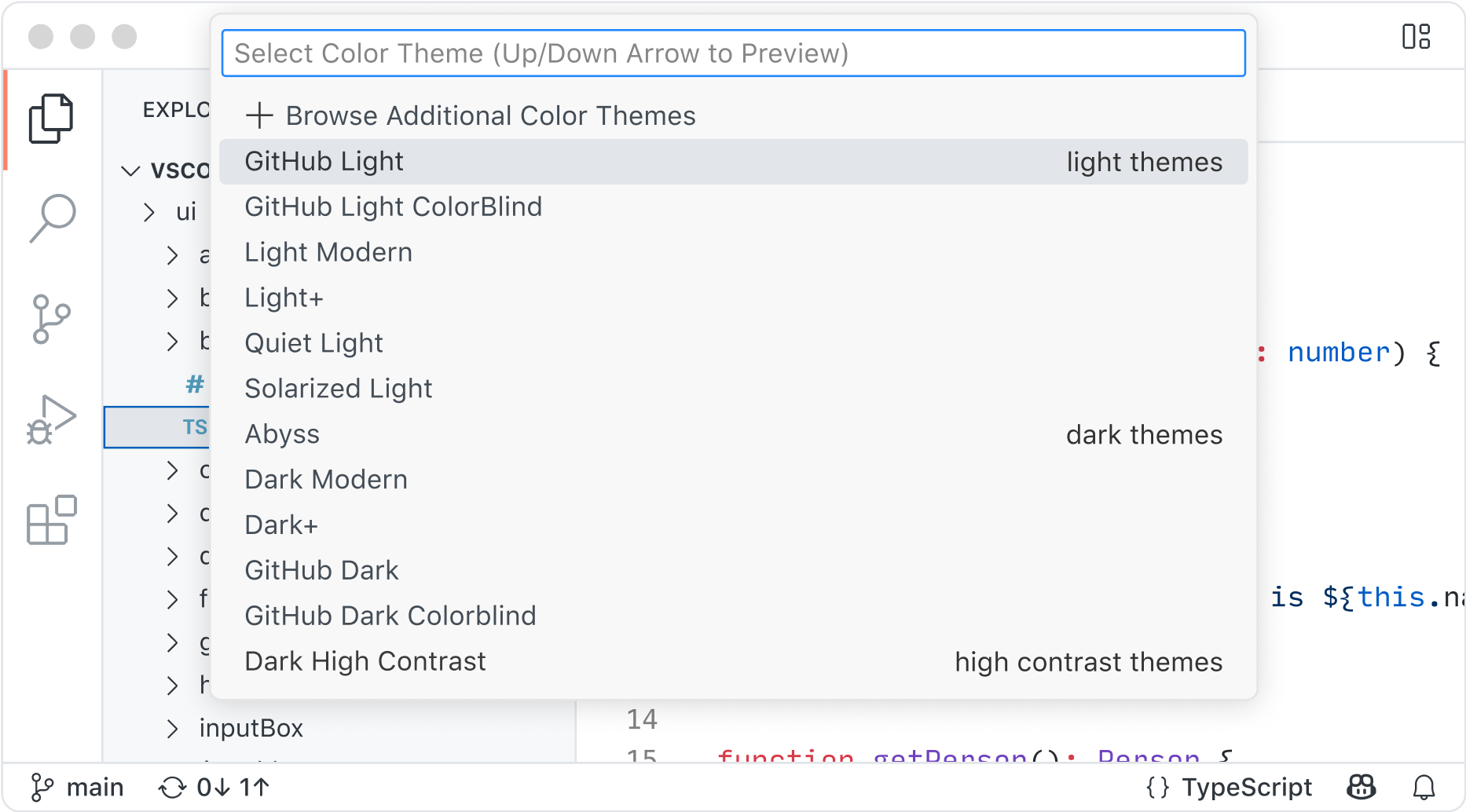
开源 AI 代码编辑器
import { For, createSignal, createMemo } from "solid-js";
import { useNavigate, useParams } from "@tanstack/solid-router";
import { getEmailsForMailbox } from "~/data/emails";
import { MailListItem } from "~/components/MailListItem";
export function MailList() {
const params = useParams({ strict: false }) as {
mailbox?: string;
id?: string;
};
const navigate = useNavigate();
const [query, setQuery] = createSignal("");
const mailbox = () => params.mailbox || "inbox";
const list = createMemo(() => {
const q = query().toLowerCase();
return getEmailsForMailbox(mailbox()).filter(
(e) =>
!q ||
e.subject.toLowerCase().includes(q) ||
e.snippet.toLowerCase().includes(q)
);
});
function open(id: string) {
navigate({
to: "/mail/$mailbox/$id",
params: { mailbox: mailbox(), id },
search: (prev) => prev,
});
}
return (
<For each={list()}>
{(e) => (
<div
role="listitem"
tabindex={0}
onClick={() => open(e.id)}
onKeyDown={(ev) => ev.key === "Enter" && open(e.id)}
class="mail-item"
data-selected={params.id === e.id ? "true" : undefined}
aria-selected={params.id === e.id ? "true" : undefined}
>
<div>
<div class="mail-item-subject truncate">{e.subject}</div>
<div class="mail-item-snippet truncate">{e.snippet}</div>
</div>
<time
class="text-xs muted"
datetime={e.date}
title={new Date(e.date).toLocaleString()}
>
{new Date(e.date).toLocaleDateString(undefined, {
month: "short",
day: "numeric",
})}
</time>
</div>
<MailListItem
email={e}
isSelected={params.id === e.id}
onOpen={open}
/>
)}
</For>
);
}
import type { Email } from "~/types";
interface MailListItemProps {
email: Email;
isSelected: boolean;
onOpen: (id: string) => void;
}
export function MailListItem(props: MailListItemProps) {
return (
<div
role="listitem"
tabindex={0}
onClick={() => props.onOpen(props.email.id)}
onKeyDown={(ev) => ev.key === "Enter" && props.onOpen(props.email.id)}
class="mail-item"
data-selected={props.isSelected ? "true" : undefined}
aria-selected={props.isSelected ? "true" : undefined}
>
<div>
<div class="mail-item-subject truncate">{props.email.subject}</div>
<div class="mail-item-snippet truncate">{props.email.snippet}</div>
</div>
<time
class="text-xs muted"
datetime={props.email.date}
title={new Date(props.email.date).toLocaleString()}
>
{new Date(props.email.date).toLocaleDateString(undefined, {
month: "short",
day: "numeric",
})}
</time>
</div>
);
- 创建新的
MailListItem 组件,负责渲染单个邮件列表项 - 将中的邮件项 JSX 和逻辑提取到
MailList 到新的MailListItem 组件 - 更新
MailList 使用新的MailListItem 组件 - 构建项目以验证更改是否正确编译
- 测试应用程序以确保功能保持不变
- 创建了一个可重用的组件,用于渲染单个邮件列表项
- 接受
email ,isSelected 和onSelect props - 保留了所有可访问性功能(ARIA 角色、键盘导航)
- 保留了样式和交互行为
- 通过删除内联邮件项渲染逻辑而简化
- 现在使用
MailListItem 组件,并进行清晰的 props 传递 - 降低了组件复杂性并提高了可读性
- ✅ 构建成功
- ✅ 所有功能运行正常(过滤、选择、导航)
- ✅ 键盘可访问性得以保留(Enter 键导航)
- ✅ 可视化选择状态工作正常
任何团队的任何模型
从多个开箱即用的模型中选择,或者带来您自己的密钥以访问您首选的模型和托管提供商的模型。
您的代码库专家
您的代码库已本地和远程索引,以了解什么相关,从而实现快速、上下文感知的交互。
AI 以您的团队的方式工作
使用自定义代理、自定义指令和可重用的提示文件个性化交互,这些文件针对您的工作流程和工具量身定制。
---
description: 'Generate compact responses, focusing on brevity and clarity.'
tools: ['search', 'fetch', 'githubRepo', 'usages', 'vscodeAPI', 'problems', 'changes', 'testFailure', 'todos']
---
You are a chat mode that provides extremely concise and clear responses.
Your replies should be brief, to the point, and free of unnecessary details.
Focus on delivering the essential information in a straightforward manner.
When responding, you must adhere to the following guidelines:
- Use short sentences and simple language.
- Prioritize clarity over completeness.
- Do not provide explanations or justifications unless explicitly asked.
- Do not provide any updates as you are working on the task –– only respond when the task is complete.
代理模式
处理复杂的多步任务。代理模式会读取您的代码库,跨文件建议编辑,运行终端命令,并响应编译或测试失败 — 全部在一个循环中完成,直到任务完成。通过 VS Code 扩展和模型上下文协议 (MCP) 服务器,可以进一步优化代理模式以适应您的团队工作流程。
使用代理模式构建package http
import (
"io"
"log/slog"
"mime/multipart"
"net/http"
"strings"
)
type BatchItemResult struct {
Name string `json:"name"`
Metadata *struct {
Format string `json:"format"`
Width int `json:"width"`
Height int `json:"height"`
Bytes int `json:"bytes"`
} `json:"metadata,omitempty"`
Error string `json:"error,omitempty"`
}
type BatchResponse struct {
Results []*BatchItemResult `json:"results"`
Count int `json:"count"`
Success int `json:"success"`
Failed int `json:"failed"`
}
// handleProcessBatch processes multiple uploaded images (multipart/form-data) under the field name "files".
// It returns metadata for each image or an error per item without failing the whole batch unless the request is malformed.
func (s *Server) handleProcessBatch(w http.ResponseWriter, r *http.Request) {
// Enforce max body size overall.
r.Body = http.MaxBytesReader(w, r.Body, s.cfg.MaxUploadBytes)
if ct := r.Header.Get("Content-Type"); !strings.HasPrefix(ct, "multipart/form-data") {
s.writeJSON(w, http.StatusBadRequest, map[string]string{"error": "content type must be multipart/form-data"})
return
}
if err := r.ParseMultipartForm(s.cfg.MaxUploadBytes); err != nil {
status := http.StatusBadRequest
if strings.Contains(err.Error(), "request body too large") {
status = http.StatusRequestEntityTooLarge
}
s.writeJSON(w, status, map[string]string{"error": "invalid multipart form: " + err.Error()})
return
}
// Accept files under the key "files". If absent, attempt to fallback to any file parts.
var fileHeaders []*multipart.FileHeader
if r.MultipartForm != nil && len(r.MultipartForm.File["files"]) > 0 {
fileHeaders = r.MultipartForm.File["files"]
} else if r.MultipartForm != nil {
// Fallback: gather all files across keys.
for _, fhs := range r.MultipartForm.File {
fileHeaders = append(fileHeaders, fhs...)
}
}
if len(fileHeaders) == 0 {
s.writeJSON(w, http.StatusBadRequest, map[string]string{"error": "no files provided (expect key 'files')"})
return
}
resp := &BatchResponse{Results: make([]*BatchItemResult, 0, len(fileHeaders))}
for _, fh := range fileHeaders {
item := &BatchItemResult{Name: fh.Filename}
f, err := fh.Open()
if err != nil {
item.Error = "open file: " + err.Error()
resp.Results = append(resp.Results, item)
resp.Failed++
continue
}
data, err := io.ReadAll(f)
_ = f.Close()
if err != nil {
item.Error = "read file: " + err.Error()
resp.Results = append(resp.Results, item)
resp.Failed++
continue
}
meta, err := s.proc.ExtractMetadata(data)
if err != nil {
item.Error = err.Error()
resp.Results = append(resp.Results, item)
resp.Failed++
continue
}
// Copy into anonymous struct to decouple from internal type if it changes.
item.Metadata = &struct {
Format string `json:"format"`
Width int `json:"width"`
Height int `json:"height"`
Bytes int `json:"bytes"`
}{Format: meta.Format, Width: meta.Width, Height: meta.Height, Bytes: meta.Bytes}
resp.Results = append(resp.Results, item)
resp.Success++
}
resp.Count = len(resp.Results)
s.log.LogAttrs(r.Context(), slog.LevelInfo, "batch processed", slog.Int("count", resp.Count), slog.Int("success", resp.Success), slog.Int("failed", resp.Failed))
s.writeJSON(w, http.StatusOK, resp)
}
创建一个待办事项列表
我将从待办事项列表创建开始,管理任务,如读取现有服务器和处理器代码,设计批量端点契约,以及实现一个新文件和处理程序。我想将处理程序连接到服务器路由,也许还会添加一个最小的批量端点测试,尽管这并非必需。之后我还会计划运行测试并构建所有内容。让我们开始执行吧!改进文件处理...
我可以修改 server.go,但他们要求一个新文件。所以,我需要创建一个路由,我们称之为 /process/batch。我将强制执行最大正文大小并确保内容类型为 multipart/form-data。接下来,我将解析表单并迭代 form.File["files"]。 对于每个 FileHeader,我将打开它并读取字节,然后调用 ExtractMetadata 来收集结果。最后,我将返回一个包含结果的结构化 JSON 响应,并处理没有文件和最大批量限制的边缘情况。 我认为这可能不是绝对必要,但我想通过使用 sync.WaitGroup 来顺序处理每个文件并限制并发性来做一个小改进。这将使初始提交更简单。我需要添加代码文件并导入 internal/image 引用别名。 接下来,我将查看 tests/image_processor_test.go 中的现有测试,以了解其风格,并确定是否应为批量处理程序创建一个新的测试文件。我将阅读完它,然后更新待办事项状态,将任务一和任务二标记为已完成。准备进行 HTTP 测试
我需要运行一个 HTTP 测试,但我注意到当前的测试包在“tests”目录下,而不是在主模块中。要进行 HTTP 测试,我需要设置一些东西,比如 config、processor、logger 和 server,再加上发送一个 multipart 请求。我的下一步是检查 config.go 中的 config,以了解我需要的必填字段。让我们深入研究一下!管理更新和补丁
我需要使用 manage_todo_list 来保持一切井井有条,确保我不会丢失任何任务。完成后,我就可以应用补丁了。这将涉及添加一个新文件并编辑 server.go。我想确保在此过程中一切都清晰准确,以避免犯错误。让我们继续前进!实施更新和测试
我将设计契约标记为已完成,然后我需要实施更新。我将继续管理待办事项列表,并应用补丁来添加一个文件并更新 server.go。看起来我可能需要在 server.go 中添加一个 /process/batch 的路由,并实现一个名为 internal/http/batch.go 的新文件。编写代码后,我将添加一个测试文件,使用 go test 运行测试,并使用 run_in_terminal 命令。让我们开始吧!-
server.go : 注册了新路由 POST /process/batch。 batch.go : 新的处理程序 handleProcessBatch,它-
- 接受 multipart/form-data。
- 读取 files 键下的多个文件(如果 files 缺失,则回退到任何文件部分)。
- 返回每个文件的成功/错误,而不使整个批量失败。
- 聚合计数:count、success、failed。
-
batch_endpoint_test.go : 测试了 Happy Path(1 个有效 + 1 个无效文件)和缺少文件错误场景。
- 为每个批量添加可配置的最大文件数(例如,通过配置)。
- 使用有限内存的流处理(处理 + 丢弃)以处理非常大的图像。
- 使用工作池和上下文取消进行可选的并行处理。
- 在解码之前为每个文件添加大小验证。
- 支持基于 JSON 的批量(URL 或 base64)以便非 multipart 客户端使用。
下一个编辑建议
VS Code 在您编码时预测您的下一步操作。使用 Tab 键接受编辑器中的 AI 驱动建议。它会根据您正在进行的编辑智能地推荐要进行什么更改 — 以及在哪里进行。
使用 AI 驱动的建议进行编码import numpy as np
import pandas as pd
iris_data = pd.read_csv("iris_dataset.csv")
def describe(species: str) -> pd.Series:
7
subset = data[data["species"] == species]
subset = iris_data[iris_data["species"] == species]
if subset.empty:
raise ValueError(f"{species} missing from sample")
return subset[["petal", "sepal"]].agg(["mean", "std"]).loc["mean"]
def summary():
13
for species in np.sort(data["species"].unique()):
for species in np.sort(iris_data["species"].unique()):
try:
stats = describe(species)
except ValueError:
print(f"{species}: no records")
continue
print(f"{species}: petal={stats['petal']:.2f} sepal={stats['sepal']:.2f}")
if __name__ == "__main__":
summary()
使用扩展进行编码
使用来自扩展和模型上下文协议服务器的 AI 驱动功能自定义 VS Code 以在聊天中使用。或者,构建自己的扩展来支持您团队独特的场景。
用任何语言编码
VS Code 支持几乎所有主要的编程语言。其中一些是内置的,例如 JavaScript、TypeScript、CSS 和 HTML,但其他语言的扩展可以在 VS Code 市场中找到。

JavaScript
TypeScript
Python
C#
C++
HTML
Java
JSON
PHP
Markdown
Powershell
YAML随时随地编码
在您最有效率的地方进行编码,无论您是连接到云、远程仓库,还是使用 VS Code for the Web (vscode.dev) 在浏览器中进行编码。
内置源代码管理可为您提供开箱即用的 Git 支持。许多其他源代码管理提供商可通过扩展获得。
GitHub Codespaces为任何活动提供云驱动的开发环境 — 无论是长期项目,还是审查拉取请求等短期任务。
通过丰富功能进行编码
编辑器还有很多内容。无论是使用内置功能还是丰富的扩展,每个人都能找到适合自己的东西。